Description
An inhibitor of Chk1 and WEE1 (IC50s = 47 and 97 nM, respectively); selective for Chk1 and WEE1 over PKC (IC50 = 3.4 µM) and Cdk4 (IC50 = 3.75 µM); selective for Chk1 and WEE1 over c-Src and the PDGF and FGF receptors (IC50s = >50 µM for all), and other Cdks (IC50s = >50 µM); sensitizes SK-OV-3 and OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cells, as well as cisplatin-resistant A2780cis cells, to cisplatin at 0.5 µM; induces myoblast differentiation into mature osteoblasts and hESC differentiation into cells with mesoderm or cytotrophoblast stem cell lineages when used in combination with BMP4
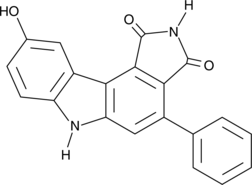
Formal name: 9-hydroxy-4-phenyl-pyrrolo[3,4-c]carbazole-1,3(2H,6H)-dione
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 328.3
CAS: 622864-54-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Checkpoint Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Other Serine/Threonine Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Stem Cell Research|Differentiation