Description
A long-chain acylcarnitine; transported into mitochondria via carnitine palmitoyl transferase II to deliver palmitate for fatty acid oxidation and energy production; inhibits lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity in rat plasma at 500 µM; increases intestinal absorption of the antibiotic cefoxitin in rat intestine,
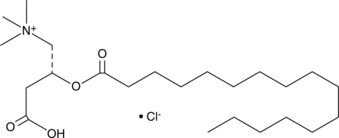
Formal name: 3-carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-2R-[(1-oxohexadecyl)oxy]-1-propanaminium, monochloride
Synonyms: Hexadecanoyl-L-carnitine|L-Hexadecanoylcarnitine|L-Palmitoylcarnitine
Molecular weight: 436.1
CAS: 18877-64-0
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Carnitines||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sterol Biosynthesis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Mitochondrial Biology||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Fatty Acids|Degradation