Description
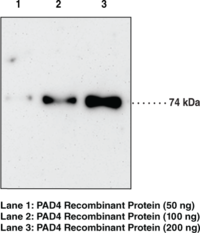
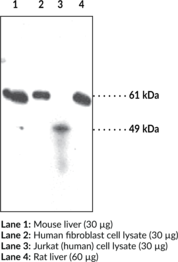
Protein arginine deiminases (PADs) are guanidino-modifying enzymes belonging to the amidinotransferase superfamily and are designated PAD1-4 and PAD6. All enzymes are cytosolic except for PAD4 which is localized in the nucleus.{18141} PAD4 is a homodimer that functions as a transcriptional coregulator to catalyze the conversion of specific arginine residues to citrulline in a calcium-dependent manner. PAD4 substrates include histones H2A, H3, and H4, whose post-translational modifications play a large role in gene regulation.{18134} Benzoylated arginine substrates like N-α-benzoyl-L-arginine ethyl ester have proven to be useful tools for characterization of PAD4, having similar kinetic properties to the natural substrates.{18133} PAD4 itself can undergo autocitrullination at several sites, which inhibits its enzymatic activity and may play an important role in regulating citrullination in cells.{18135} PAD4 activity is increased in rheumatoid arthritis, producing an abundance of citrulline-containing proteins that can be recognized by autoantibodies, causing the immune system to attack its own tissues.{18137} PAD4 has also been implicated in several other diseases including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, glaucoma, and cancer.{18134} The predicted size of PAD4 is 74.1 kDa and Cayman’s PAD4 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 11F9) detects a band at 74 kDa by western blot.
Synonyms: Protein-arginine Deiminase type-4|HL-60 PAD|PADI4|Peptidylarginine Deiminase IV
Immunogen: Full length recombinant PAD4 protein
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified IgG
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA, WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Writers|Citrullination||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease