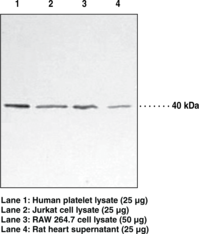
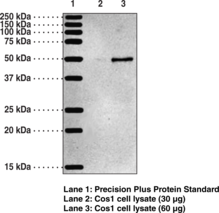
Description
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a member of the serine-threonine MAPK family that triggers many cellular processes including cell cycle, development, and apoptosis.{15420,15421} These kinases are activated by environmental stress signals such as osmotic shock, infection, and cytokines causing phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. This results in a phosphorylation cascade, activating transcription factors, and inducing gene expression.{15420,15424} p38 MAPK is widely expressed in heart, brain, skeletal muscle, platelets, and immune cells. Due to this distribution, p38 MAPK plays a role in cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and cancer.{15421,15422,1523,15424} It is mainly present in the cytosol, but can also be found in the nucleus after activation.{15421} Based on the amino acid sequence, the expected molecular weight of this protein is 41 kDa.
Synonyms: p38 MAP Kinase|p38 MAPKα|p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
Immunogen: human full length p38 MAPK
Formulation: 200 µg IgG1 in 500 µl PBS, pH 7.4, containing 50% glycerol, 0.5 mg/ml BSA, and 0.02% sodium azide
Isotype:
Applications: WB, ICC, and flow cytometry
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 365 days
Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|p38 MAPK Signaling||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Heart||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Cycle||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|p38 MAPK Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis||Research Area|Infectious Disease