Description
An L-type calcium channel blocker; selective for L-type over N-, P/Q-, and R-type calcium channels at 10 μM; inhibits increases in systolic blood pressure induced by chronic intravenous infusion of endothelin in rats at 10 mg/kg per day, p.o.; decreases cortical and hippocampal amyloid-β burden in the APPsw (Tg2576) and PS1/APPsw transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease at 0.03% (w/w) in the diet for 17 and 10 months, respectively; reduces infarct volume in a rat model of MCAO-induced focal cerebral ischemia at 3.2 mg/kg, s.c.
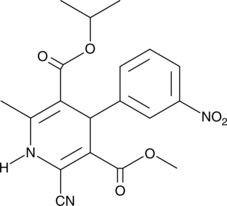
Formal name: 2-cyano-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 3-methyl 5-(1-methylethyl) ester
Synonyms: (±)-Nilvadipine|CL 287,389|FK-235|FR34235|SKF 102362
Molecular weight: 385.4
CAS: 75530-68-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Ion Channel Modulation|Blockers||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Hypertension||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Stroke||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia