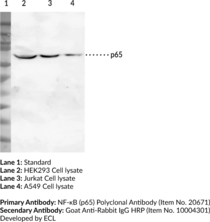
Description
NF-κB p65 is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor that is a subunit of the NF-κB complex and is encoded by the RELA gene in humans.{53059} It is composed of an N-terminal Rel homology domain, which mediates dimerization, nuclear localization, and DNA and protein interactions, and two C-terminal transactivation domains that are subject to a variety of post-translational modifications and regulate the transcriptional activity of p65.{53059,53060} NF-κB p65 regulates the expression of a large number of genes in response to inflammatory and environmental cues that play critical roles in innate and adaptive immunity and cellular differentiation.{53060} Genome-wide deletion of Rela in mice is embryonic lethal.{5321} Silencing of NF-κB p65 induces tumor cell apoptosis in a murine Lewis lung carcinoma model and decreases secreted levels of IL-1β and TNF-α induced by LPS in THP-1 monocytes.{53061,53062} NF-κB p65 is overexpressed in inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and naïve CD4 T cells isolated from the whole blood of patients with multiple sclerosis have increased phosphorylation of NF-κB p65.{53065,53066} Cayman’s NF-κB p65 (human, recombinant) protein can be used for Western blot and ELISA applications. Cayman’s NF-κB (p65) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes NF-κB at 65 kDa from human samples.
Synonyms: Nuclear Factor NF-κB (p65) subunit|Transcription Factor p65
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the C-Terminal region of human NF-κB (p65)
Formulation: 500 µl of peptide affinity-purified antibody
Isotype: IgG
Applications: ELISA and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Transcription Factors|NF-κB||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Pattern Recognition||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|STING||Research Area|Infectious Disease