Description
An inhibitor of mutant EGFRs; selective for EGFR mutant cell lines, including H3255 and HCC827 lung adenocarcinoma cells (IC50s = 6.11 and 1.52 nM, respectively) and resistant H1975 NSCLC cells (IC50 = 4.18 nM), over cells expressing wild-type EGFR (IC50 = 160.6 nM for HaCaT keratinocytes); decreases phosphorylation of EGFR in H3255, HCC827, and H1975 cells (EC50s = 5, 1, and 3 nM) and inhibits cell proliferation of H3255, HCC827, and H1975 cells (EC50s = 9, 11, and 25 nM) but does not affect cell proliferation in cell lines containing wild-type EGFR; reduces tumor growth in an HCC827 lung adenocarcinoma mouse xenograft model at doses ranging from 3 to 100 mg/kg per day
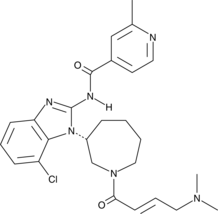
Formal name: N-[7-chloro-1-[(3R)-1-[(2E)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-buten-1-yl]hexahydro-1H-azepin-3-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-2-methyl-4-pyridinecarboxamide
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 495
CAS: 1508250-71-2
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|EGFR/ErbB/HER Family||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Multidrug Resistance