Description
A metabolite of rivastigmine
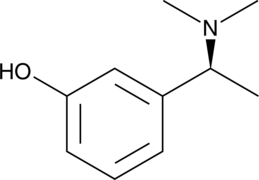
Formal name: 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-phenol
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 165.2
CAS: 139306-10-8
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Available on backorder
A metabolite of rivastigmine
Formal name: 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-phenol
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 165.2
CAS: 139306-10-8
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC (DPPC) is a zwitterionic glycerophospholipid commonly used in the formation of lipid monolayers, bilayers, and liposomes for use in a variety of applications.{14480,24261,14478,14479} It has been used in the formation of proteoliposomes for implantation of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase into human erythrocyte membranes.{14478} Incorporation of glycosphingolipid antigens into DPPC-containing liposomes increases the immunogenicity of the antigens in mice.{14479}
Available on backorder
The tetracycline repressor (TetR) is a transcriptional regulator which normally binds tightly to its palindromic tetO operator DNA, blocking gene expression.{17508} Tet causes the repressor to dissociate from the DNA, allowing transcription to occur. A novel reverse TetR (revTetR) requires tetracycline as a co-repressor to bind tetO and block transcription.{17509,17510} Anhydrotetracycline (hydrochloride) is a powerful effector in both the tetracycline repressor (TetR) and reverse TetR (revTetR) systems, binding the Tet repressor 35-fold more strongly than Tet.{17508,17511} Moreover, anhydrotetracycline poorly binds the 30S ribosomal subunit, compared to Tet,{17512} so it does not act as a general inhibitor of translation and is a poor antibiotic. Perhaps related to this, the concentration of anhydrotetracycline that inhibits eukaryotic cell growth is more than a 1,000-fold above the dose that alters transcription through TetR.{17508}
Available on backorder
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC (DPPC) is a zwitterionic glycerophospholipid commonly used in the formation of lipid monolayers, bilayers, and liposomes for use in a variety of applications.{14480,24261,14478,14479} It has been used in the formation of proteoliposomes for implantation of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase into human erythrocyte membranes.{14478} Incorporation of glycosphingolipid antigens into DPPC-containing liposomes increases the immunogenicity of the antigens in mice.{14479}
Available on backorder
The PtdIn phosphates play an important role in the generation and transduction of intracellular signals.{8344,4096,14518} PtdIns-(3,4,5)-P3-biotin is an affinity probe which allows the PIP3 to be detected through an interaction with the biotin ligand. This design allows PtdIns-(3,4,5)-P3-biotin to serve as a general probe for any protein with a high affinity binding interaction with inositol-(3,4,5)-triphosphate phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PTEN, or PH-domain-containing proteins.
Available on backorder