Description
An inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase, GBA, GBA2, acid α-glucosidase, sucrase, maltase, and lactase; reduces glycolipid levels in HL-60 and WEHI-3B cells from 0.5-500 µM; decreases brain ganglioside levels in a Glb1-/-neonatal mouse model of GM1 gangliosidosis at 600 and 1,200 mg/kg four times per day for three days; increases testicular glucosylceramide levels in mice from 1-1,200 mg/kg per day for 35 days; induces abnormal spermatid and acrosome formation, as well as reduces motility, in isolated mouse epididymal sperm at 15, 25, and 50 mg/kg per day; induces infertility, an effect that is reversed by withdrawal, in the same model
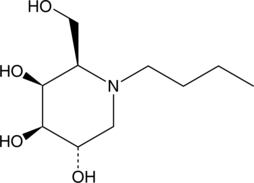
Formal name: 1-butyl-2R-(hydroxymethyl)-3S,4R,5S-piperidinetriol
Synonyms: Lucerastat|NBDGJ
Molecular weight: 219.3
CAS: 141206-42-0
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sphingolipid Turnover||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Carbohydrate Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Inborn Errors of Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Reproductive Biology||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sphingolipids