Description
An ATP-competitive, allosteric inhibitor of IRE1α RNase kinase activity (IC50 = 0.6 µM); prevents IRE1α oligomerization and promotes cell survival under ER stress in rat models of retinal degeneration and diabetes
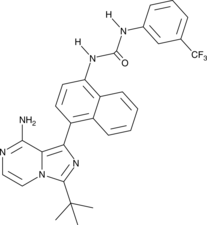
Formal name: N-[4-[8-amino-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)imidazo[1,5-a]pyrazin-1-yl]-1-naphthalenyl]-N’-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-urea
Synonyms: IRE1 Inhibitor IV|IRE1α Kinase Inhibiting RNase Attenuator 6
Molecular weight: 518.5
CAS: 1589527-65-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Other Serine/Threonine Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cell Biology|Endomembrane System & Vesicular Trafficking||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes