Description
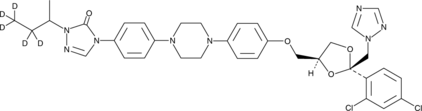
An internal standard for the quantification of itraconazole by GC- or LC-MS
Formal name: 4-(4-(4-(4-(((2R,4S)-2-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-2-(butan-2-yl-3,3,4,4,4-d5)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 710.7
CAS: 1217510-38-7
Purity: ≥99% deuterated forms (d1-d5)
Formulation: A solid
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Analytical Standards||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antifungals|Triazoles||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antivirals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Isotopically Labeled Standards|Deuterium||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sterol Biosynthesis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Hedgehog Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Hedgehog Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Fungal Diseases|Aspergillosis||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|Rhinoviruses