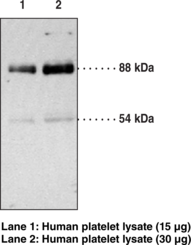
Description
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is a ubiquitous transcription factor and an essential mediator of gene expression during activation of immune and inflammatory responses. NF-κB mediates the expression of a great variety of genes in response to extracellular stimuli including IL-1, TNF-α, and LPS. A serine/threonine protein kinase associated with interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1) and its homologue murine pelle-like protein kinase (mPLK) has been identified.{10659,18740} IRAK-1 is associated with the IL-1 receptor subunits IL-1RI and IL-1RAcP after IL-1 binding and serves as a signaling molecule to mediate IL-1 response.{18739} IRAK-1 mediates a signaling cascade leading to NF-κB activation by members of the IL-1 family including IL-1 and IL-18 (also known as IGIF).{2150,18740}
Synonyms: Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 1
Immunogen: synthetic peptide corresponding to human IRAK-1 amino acids 700-712
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified IgG in 200 µl PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Isotype:
Applications: IP and WB
Origin:
Stability: 180 days
Application|Immunoprecipitation||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation