Description
Potent, cell permeable inhibitor of PHD2 (IC50 = 21 nM) with over 100-fold selectivity compared to inhibition of JMJD2A, JMJD2C, JMJD2E, JMJD3, or the 2OG oxygenase FIH (IC50s > 100 μM); inhibits HIF-1α hydroxylation in RCC4 cells at 50 μM
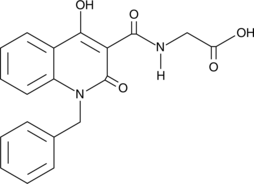
Formal name: N-[[1,2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(phenylmethyl)-3-quinolinyl]carbonyl]-glycine
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 352.3
CAS: 931398-72-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors