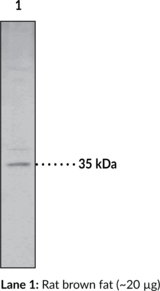
Description
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, is expressed by many cell types following pro-inflammatory stimulation and is thought to be released on cell lysis. The 30 kDa human IL-33 is converted by CASP1 to a 18 kDa protein. IL-33 binds to and signals through ST2 (IL1R1) and its stimulation recruits MYD88, IRAK, IRAK4, and TRAF6, followed by phosphorylation of ERK1 (MAPK3)/ERK2 (MAPK1), p38 (MAPK14), and JNK. The ability of IL-33 to target numerous immune cell types, like Th2-like cells, mast cells, and B1 cells, and to induce cytokine and chemokine production underlines its potential in influencing the outcome of a wide range of diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, atopic allergy and anaphylaxis, cardiovascular disease/atherosclerosis, nervous system diseases, and sepsis.
Synonyms: IL-1F11|IL-33|NF-HEV
Immunogen: recombinant human IL-33
Formulation: A 1 mg/ml solution in PBS, pH 7.4
Isotype: IgG1κ
Applications: ELISA, IP, and WB
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 180 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Immunoprecipitation||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Allergy||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Arthritis (Non-autoimmune)||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Sepsis/Shock||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases|Asthma