Description
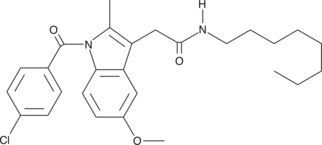
Indomethacin is a potent but non-selective inhibitor of both COX-1 and COX-2 in sheep and humans.{1286} Structurally, indomethacin is a substituted indole acetic acid, wherein the carboxylate can be derivitized as an ester or amide. These derivatives show enhanced selectivity for the COX-2 isoform. For example, the IC50 values of indomethacin N-octyl amide for the inhibition of ovine COX-1 and human recombinant COX-2 are 66 µM and 40 nM, respectively, making it 1,650 times more potent as an inhibitor of COX-2 than COX-1.{8243} While indomethacin itself has an IC50 of 0.05 µM for the inhibition of COX-2, it also inhibits COX-1 with a corresponding IC50 of 0.67 µM.
Formal name: N-octyl-1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indole-3-acetamide
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 469
CAS: 282728-65-8
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid