Description
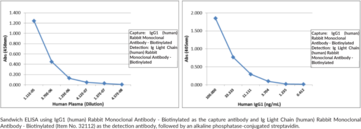
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG1 binds to Fc receptors to induce Fc receptor-mediated effector functions, as well as Cq1 to induce complement activation in response to soluble and membrane protein antigens. Maternal IgG1s are shared with the fetus via placental transfer and children with group B streptococcal-induced sepsis are born to mothers with decreased serum levels of IgG1 compared with mothers of uninfected children.{53928} Cayman’s IgG1 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody – Biotinylated can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the heavy chain of human IgG1.
Synonyms: Immunoglobulin IgG1
Immunogen: Peptide from the hinge region of human IgG1
Formulation: 50 µg of protein A-affinity purified monoclonal antibody
Isotype: IgG
Applications: ELISA, ICC, and IHC
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Serum Proteins||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Reproductive Biology||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Sepsis/Shock||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases