Description
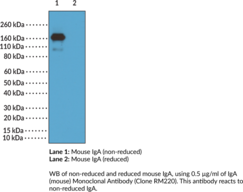
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins with roles in host defense against intestinal pathogens and both quantitative and qualitative control of host commensal microbiota composition.{53918,53919} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant antibody on mucosal surfaces that comprises at least 70% of all Ig produced in mice. Mouse IgA consists of two heavy chains of approximately 53.5 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53917} Unlike human IgA, mouse IgA exists as a single isotype and is primarily found as a dimer that lacks the disulfide bonds between the light and heavy chains present in other Ig classes.{53917,53920} Production of IgA is induced in the gut only in animals containing intestinal microbes, and the number of IgA-producing plasma cells is reduced in germ-free mice.{53918} IgA-deficient mice exhibit increased lethality compared with wild-type mice in a model of influenza infection, as well as reduced bacterial clearance in a model of G. muris infection. However, IgA deficiency does not affect clearance of vaginal infection with herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2), indicating redundancy in pathogen protection with compensation by antibodies of other isotypes or innate immune mechanisms at mucosal surfaces. Cayman’s IgA (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM220) can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes IgA at approximately 160 kDa from mouse samples.
Synonyms:
Immunogen: Mouse IgA
Formulation: 100 µg of protein A-affinity purified monoclonal antibody
Isotype: IgG
Applications: ELISA, WB (non-reducing conditions)
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Serum Proteins||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|HSV||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|Influenza