Description
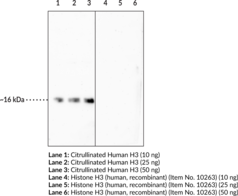
Histones are nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. The basic structure is a 146 bp strand of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer containing pairs of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). Histones are subjected to numerous post-translational modifications including citrullination (de-imination). Citrullination is necessary for the development of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (hyper-citrullination of histones by PAD4).{28015,28019} NETs are a part of the inflammatory response, and neutrophils use NETs to trap and eradicate bacteria and fungi. Failure to clear citrullinated proteins and NET components following inflammation can result in the production of autoantibodies and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies.{28017} The persistence of these antibodies and citrullinated proteins is associated with a number of human diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.{28018} The ability to effectively detect the presence of citrullinated proteins is difficult and presents a barrier to further the understanding of these pathologies. Cayman’s Histone H3 (Citrullinated R2 + R8 + R17) Monoclonal Antibody detects citrullinated human H3 by western blot, and does not detect unmodified H3.
Synonyms:
Immunogen: histone 3 peptide with citrullinations at R2, R8, and R17
Formulation: 100 µg protein G-purified IgG
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Histones/Histone Peptides|Citrullinated||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Writers|Citrullination||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation