Description
A prodrug formulation of HPA which may be useful in various biochemical studies and as a reference standard in analytical work
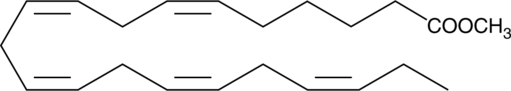
Formal name: 6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z-heneicosapentaenoic acid, methyl ester
Synonyms: HPA methyl ester
Molecular weight: 330.5
CAS: 65919-53-1
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Analytical Standards||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Fatty Esters/Ethers||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Prostaglandin Synthases||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Fatty Acids