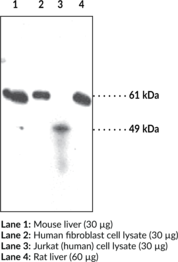
Description
Cyclooxygenase (COX) catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes, and prostacyclins: the conversion of arachidonic acid to PGH2. Discoveries of the induction of COX by a variety of stimuli such as phorbol esters, lipopolysaccharides, and cytokines led to the hypothesis that the inducible form of COX, COX-2, is responsible for the biosynthesis of PGs under acute inflammatory conditions.{4,3463} COX-2 is a 72 kDa protein which has been cloned from a variety of species including human, mouse, rat, and ovine.{2,7,2884,4051}
Synonyms: Cyclooxygenase-2|PGHS-2|Prostaglandin H Synthase-2
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the C-terminal region of human COX-2
Formulation: 500 µl of peptide affinity-purified IgG
Isotype:
Applications: IF, IHC, and WB
Origin: Animal/Goat
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway