Description
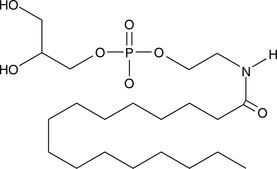
Precursor of PEA, an endogenous CB found in brain, liver, and other mammalian tissues; PEA has potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo
Formal name: mono(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-mono[2-[(1-oxohexadecyl)amino]ethyl]ester phosphoric acid
Synonyms: GP-NAE|GP-NPEA
Molecular weight: 453.6
CAS: 100575-09-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Fatty Amides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Endocannabinoid/Endocannabinoid-like||Research Area|Neuroscience|Cannabinoid Research|CB1 & CB2 Receptors||Research Area|Neuroscience|Cannabinoid Research|Endocannabinoids