Description
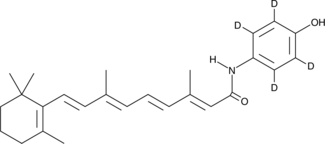
An internal standard for the quantification of fenretinide by GC- or LC-MS
Formal name: N-(4-hydroxyphenyl-2,3,5,6-d4)-retinamide
Synonyms: 4-HPR-d4|4-Hydroxy(phenyl)retinamide-d4|Retinoic Acid p-hydroxyphenylamide-d4
Molecular weight: 395.6
CAS: 2118244-64-5
Purity: ≥99% deuterated forms (d1-d4)
Formulation: A solid
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Analytical Standards||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Activators||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Fatty Acid Metabolism||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sphingolipid Turnover||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Hormones & Receptors|RARs, RORs, & RXRs||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes