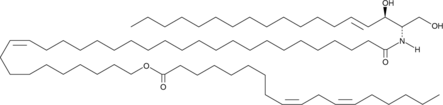
Description
An essential ceramide for prevention of epidermal water loss; found in the outer epidermis of mammals; consecutive regio- and stereospecific oxygenation of the linoleate portion by 12(R)-LO and eLOX3 is essential for the maintenance of the epidermal barrier to prevent water loss
Formal name: 9Z,12Z-octadecadienoic acid, (10Z)-32-[[(1S,2R,3E)-2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-3-heptadecen-1-yl]amino]-32-oxo-10-dotriaconten-1-yl ester
Synonyms: C52:3 EOS (18:1/32:1(22 Z)w18:2(9Z,12Z)|Esterified ω-hydroxyacyl Sphingosine
Molecular weight: 1,038.80
CAS: 1318771-31-1
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in dichloromethane
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Sphingolipids||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Lipoxygenase Pathways||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sphingolipids