Description
A protease inhibitor with diverse biological activities; inhibits calpain and the cysteine proteases cathepsins F, -K, -B, -H, and -L; induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells from 20-200 µM; inhibits protease-resistant prion protein accumulation in scrapie-infected neuroblastoma cells (IC50 = 0.5 µM); inhibits SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 surface glycoprotein incorporation into pseudotyped VSV particles in Vero cells
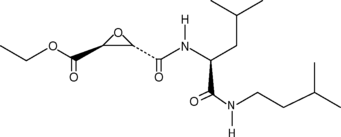
Formal name: 3-[[[(1S)-3-methyl-1[[(3S-methylbutyl)amino]carbonyl]butyl]amino]carbonyl]-2S-oxiranecarboxylic acid, ethyl ester
Synonyms: Aloxistatin|E-64c ethyl ester|EP 453|EST|Loxistatin|NSC 694281
Molecular weight: 342.4
CAS: 88321-09-9
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antivirals|Protease Inhibitors||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Peptidases & Proteases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle|G2/M||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Lysosomal Proteases||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases|COVID-19||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases|MERS||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|Coronaviruses||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Prion Disease