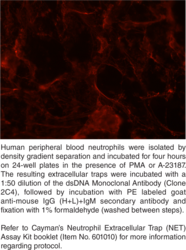
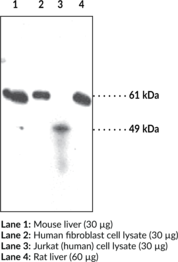
Description
In response to stimuli, neutrophils have the ability to release net-like structures containing nuclear DNA, de-condensed histones, and antimicrobial peptides.{19770} These neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) have the ability to contact and kill pathogens including fungi, bacteria, and protozoa; they are then rapidly cleared by the immune system.{24590,24587,25672} However, in aged NZBWF1 mice and human lupus patients, the clearance is delayed, allowing formation of antibodies to these NET components. Cayman’s dsDNA Monoclonal Antibody was developed by fusing the spleen of a non-immunized NZBWF1 mouse with a mouse myeloma cell line. It detects dsDNA by ELISA and can be used to stain NETs by immunofluorescence.
Synonyms: double-stranded DNA
Immunogen:
Formulation: 200 µg of ammonium sulfate-purified monoclonal
Isotype: IgM
Applications: ELISA, FC, IHC, and IF
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunofluorescence||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Lupus||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|NETosis||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Fungal Diseases||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Parasitic Diseases