Description
A tumor vascular disrupting agent, inducing apoptosis in tumor vascular endothelium resulting in necrosis at the tumor core; potently activates the STING/TBK1/IRF3 signaling pathway in mouse leukocytes, inducing type-I-IFN production; inhibits VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 (IC50 = 119 and 11 µM, respectively)
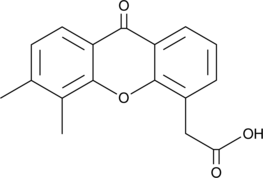
Formal name: 5,6-dimethyl-9-oxo-9H-xanthene-4-acetic acid
Synonyms: 5,6-Dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic Acid|ASA 404|NSC 640488|Vadimezan
Molecular weight: 282.3
CAS: 117570-53-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Other Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Angiogenesis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptors||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Pattern Recognition||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|STING||Research Area|Infectious Disease