Description
An anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, and antibacterial compound; reduces epidermal hyperproliferation and epithelial thickness in the esophagus in a mouse model of proliferative dermatitis when administered at a dose of 34 μg/animal per day; reduces lipid peroxidation, myeloperoxidase activity, and cellular apoptosis in the striatum of rats following ischemia and reperfusion injury; reduces growth of M. leprae in the footpad of mice (MIC = 0.01-0.03 μg/ml in sera); induces clearance of P. knowlesi infections in macaques; reduces the number of P. gallinaceum sporozoites in a mosquito population allowed to feed on dapsone-treated chicks,
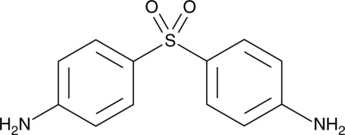
Formal name: 4,4′-sulfonylbis-benzenamine
Synonyms: 4,4′-Diaminodiphenyl sulfone|NSC 6091
Molecular weight: 248.3
CAS: 80-08-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antiparasitics|Antiprotozoals||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Leprosy||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Parasitic Diseases||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia