Description
DAF-2 diacetate is a sensitive fluorescent indicator for the detection and bioimaging of NO.{6360,6632} It is a cell-permeable derivative of DAF-2. Upon entry into the cell, DAF-2 diacetate is transformed into the less cell-permeable DAF-2 by cellular esterases thus preventing loss of signal due to diffusion of the molecule from the cell. In the presence of oxygen, DAF-2 reacts with NO to yield the highly fluorescent triazolofluorescein (DAF-2T). Fluorescence is monitored using excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 538 nm, respectively.{6632} At neutral pH the detection limit for NO is 2-5 nM. DAF-2 diacetate can be utilized in cells which produce small amounts of NO, such as endothelial cells, as well as in cells which generate large amount of NO, such as macrophages.{6360,6632}
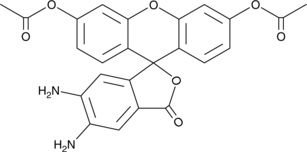
Formal name: 2-(3,6-diacetyloxy-4,5-diamino-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-benzoic acid
Synonyms: 4,5-Diaminofluorescein diacetate
Molecular weight: 446.4
CAS: 205391-02-2
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in DMSO