Description
A glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor; inhibits glucosylceramide synthase by 50% at a 5 µM in an enzyme assay; the active component of racemic DL-threo-PDMP; inhibits the synthesis of glucosylceramide synthase and lactosylceramide in B16 melanoma cells at 25 µM; inhibits B4GALT6 and prevents lactosylceramide synthesis; inhibits ganglioside biosynthesis, reduces long-term potentiation (LTP) in mouse hippocampal CA1 neurons, and impairs learning in the four-pellet taking test in mice
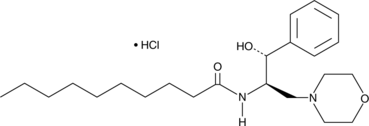
Formal name: N-[(1R,2R)-2-hydroxy-1-(4-morpholinylmethyl)-2-phenylethyl]-decanamide, monohydrochloride
Synonyms: D-PDMP
Molecular weight: 427
CAS: 139889-62-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sphingolipid Turnover||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sphingolipids||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory