Description
A sesquiterpene alcohol with diverse biological activities; a PAM of GABAA receptors that potentiates GABA-induced currents in hippocampal neurons; reduces activation of proinflammatory NF-κB and profibrotic TGF-β1/SMAD signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with cigarette smoke extract from 1-200 μg/ml; inhibits proliferation of and induces apoptosis in LoVo and SW480 colorectal cancer cells; reduces tumor volume in a LoVo mouse xenograft model from 20-80 mg/kg; increases the rate of wound closure in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes
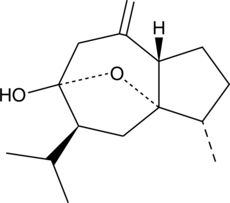
Formal name: (3S,3aS,5S,6R,8aS)-octahydro-3-methyl-8-methylene-5-(1-methylethyl)-6H-3a,6-epoxyazulen-6-ol
Synonyms: (−)-Curcumol
Molecular weight: 236.4
CAS: 4871-97-0
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Terpenes||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Allosteric Modulators||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|TNF-α/NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Neuroscience