Description
An inhibitor of LGPa, MGPa, and MGPb (IC50s = 0.13, 0.2, and 0.3 μM, respectively, in the presence of glucose); inhibits glucagon-stimulated glycogenolysis in primary human hepatocytes (IC50 = 2.1 μM) and increases glycogen synthesis in rat hepatocytes at a concentration of 2.5 μM in the presence of 5 mM glucose; inhibits brain GP (IC50 = 0.5 μM) and glycogen accumulation and proliferation of A549 NSCLC cells that express endogenous brain GP (30 μM); lowers plasma glucose level in diabetic ob/ob mice within 3 hours of administration without producing hypoglycemia, but has no effect on normoglycemic, non-diabetic mice (25 mg/kg, p.o.)
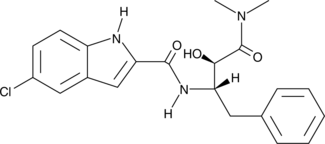
Formal name: 5-chloro-N-[(1S,2R)-3-(dimethylamino)-2-hydroxy-3-oxo-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-1H-indole-2-carboxamide
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 399.9
CAS: 186392-40-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors||Research Area|Cancer|Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes