Description
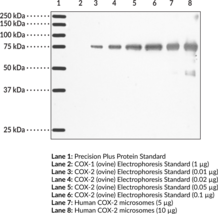
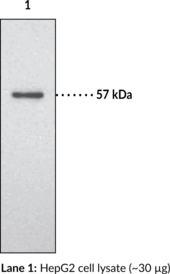
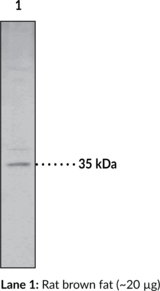
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) is a bifunctional enzyme that exhibits both COX and peroxidase activities and catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and prostacyclins.{500,501} The COX component converts arachidonic acid to the hydroperoxy endoperoxide prostaglandin G2 (PGG2; Item No. 17010), and the peroxidase component reduces the endoperoxide to the corresponding alcohol PGH2 (Item No. 17020). COX2 expression is induced by a variety of stimuli, including phorbol esters, LPS, and cytokines and is responsible for the biosynthesis of PGs under acute inflammatory conditions.{54420,14766} Thus, COX-2 has been the focus of attention for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) development. Cayman’s COX-2 (human) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone CX229) can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes a unique C-terminal region of COX-2 that is not present in COX-1, specifically detecting COX-2 ~70 kDa from human and ovine samples.
Synonyms: Cyclooxygenase 2|PGHS-2|Prostaglandin H Synthase 2
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the C-terminal region of human protein COX-2
Formulation: 50 µg of protein G-purified antibody
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: IHC, WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Inflammatory Lipid Mediators|Prostaglandins||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway