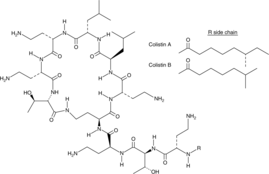
Description
An antibiotic; inhibits the growth of a variety of Gram-negative (MICs = 0.04-2.08 µg/ml) and some Gram-positive bacteria (MICs = 2.5-10 µg/ml); inhibits the growth of clinical isolates of both susceptible and multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa (MICs = 1-2 mg/l); binds selectively to LPS from susceptible strains of K. pneumoniae compared to resistant strains (Kis = 0.56 and 2.83 µM, respectively); inhibits growth of P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii strains in a neutropenic mouse model of thigh infection
Formal name:
Synonyms: Polymyxin E Complex
Molecular weight: 1,169.50
CAS: 1066-17-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics|Polypeptides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Microbial Metabolites||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Food-borne Illnesses||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Pneumonia||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Typhoid