Description
An internal standard for the quantification of ciprofloxacin by GC- or LC-MS
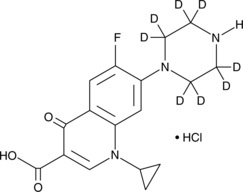
Formal name: 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl-2,2,3,3,5,5,6,6-d8)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, monohydrochloride
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 375.9
CAS: 1216659-54-9
Purity: ≥99% deuterated forms (d1-d8)
Formulation: A solid
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Analytical Standards||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics|Quinolones & Fluoroquinolones||Product Type|Biochemicals|Isotopically Labeled Standards|Deuterium||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Food-borne Illnesses||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Pneumonia||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|STDs