Description
An agonist of S1P1 and S1P5 receptors (Kis = 0.626 and 0.574 nM, respectively); selective for S1P1 and S1P5 over S1P2-4 (Kis = >5,450, >5,630, and 28.8 nM, respectively); induces calcium influx in CHO-K1 cells overexpressing S1P1 (EC50 = 1 nM) and cAMP accumulation in CHO-K1 cells overexpressing S1P1 or S1P5 (EC50s = 0.027 and 0.33 nM, respectively); reduces paw edema in a rat model of CIA at 0.03 and 0.1 mg/kg; delays disease onset and inhibits lymphocyte infiltration of the spinal cord in a rat model of EAE; prevents disease relapse in a non-obese diabetic mouse model of relapsing-remitting EAE
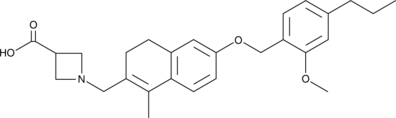
Formal name: 1-[[3,4-dihydro-6-[(2-methoxy-4-propylphenyl)methoxy]-1-methyl-2-naphthalenyl]methyl]-3-azetidinecarboxylic acid
Synonyms: ONO-4641
Molecular weight: 435.6
CAS: 891859-12-4
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders