Description
An antibiotic; active against various bacterial strains, including M. tuberculosis, and trypanosomes; inhibits proliferation of EBV-transformed cells, activates the c-Myc and NF-κB pathways in vitro, and induces necrotic cell death in gammaherpes virus-infected B cells; protective against bacterial leaf blight in rice plants (100-200 ppm); inhibits α-ketoglutarate in X. oryzae (1 ppm)
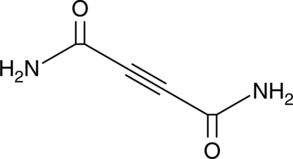
Formal name: 2-butynediamide
Synonyms: Acetylenedicarboxylic Acid|NSC 38643|NSC 65381
Molecular weight: 112.1
CAS: 543-21-5
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antiparasitics|Antiprotozoals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Microbial Metabolites||Product Type|Biochemicals|Pesticides||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Tuberculosis||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Parasitic Diseases|African Sleeping Sickness||Research Area|Plant Biology|Phytoprotectants