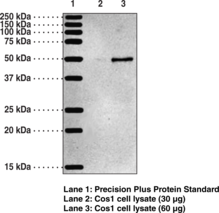
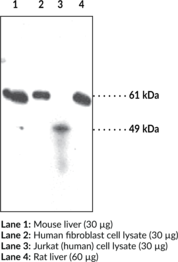
Description
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells and thereby atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800,9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate PPARγ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} Positive controls include adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages. Cayman’s CD36 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone JC63.1) (azide free) can be used for flow cytometry, functional blocking, and immunocytochemistry applications.
Synonyms: Fatty Acid Translocase|GPIIIb|GPIV|PAS IV|Platelet Collagen Receptor|Platelet Glycoprotein 4|Thrombospondin Receptor
Immunogen: Recombinant adenovirus expressing full-length mouse CD36
Formulation: 100 μg or 500 μg of purified IgA
Isotype: IgA
Applications: FC, functional blocking, and ICC
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 365 days
Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Erythrocytes & Hemoglobin||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Atherosclerosis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Lipids & Lipoproteins|Lipoproteins||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Phagocytosis||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Parasitic Diseases|Malaria||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Lipid Peroxidation