Description
A potent Chk1 inhibitor (IC50 = 8 nM); selective for Chk1 over FLT3, Chk2, and CDK1 (IC50s = 600, >10,000, and >10,000 nM, respectively) as well as a panel of 121 additional kinases at 10 μM; reverses cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase induced by etoposide and SN-38 in HT-29 cells and gemcitabine in SW620 cells; potentiates the genotoxicity of SN-38, gemcitabine, and etoposide in HT-29, SW620, MiaPaCa-2, and Calu-6 cells; in combination with irinotecan or gemcitabine, increases the delay of tumor growth in SW620 and Calu-6 mouse xenograft models, respectively, at 75 mg/kg
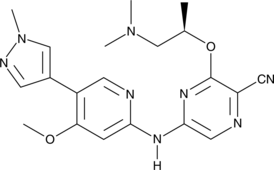
Formal name: 3-[(1R)-2-(dimethylamino)-1-methylethoxy]-5-[[4-methoxy-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-2-pyridinyl]amino]-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 408.5
CAS: 1404095-34-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Checkpoint Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle|G2/M||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling