Description
An orally bioavailable noncompetitive inhibitor of GLS1; inhibits GAC (IC50s 50s = 28 and 23 nM, respectively for brain and kidney) compared to GLS2 (IC50 > 1,000 nM for liver); antiproliferative against TNBC cell lines HCC1806 and MDA-MB-231 (IC50s = 49 and 26 nM, respectively), but not against estrogen receptor-positive cells T47D (IC50 > 1,000 nM); inhibits tumor growth by 61% in a patient-derived TNBC xenograft model (200 mg/kg, p.o.); antiproliferative against AML and in synergy with erlotinib against EGFR-driven NSCLC
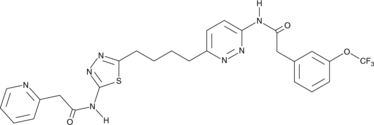
Formal name: N-[5-[4-[6-[[2-[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]acetyl]amino]-3-pyridazinyl]butyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]-2-pyridineacetamide
Synonyms: GLS1 Inhibitor III
Molecular weight: 571.6
CAS: 1439399-58-2
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Amino Acid Turnover||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Metabolism