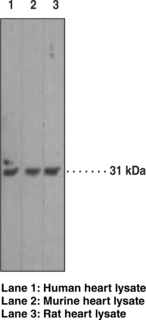
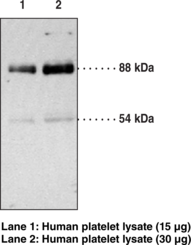
Description
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{18384} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation, and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into a tetramer to form the active enzyme. The gene for caspase-3 also known as Yama, CPP32, and apopain codes for a 32 kDa protein.{8444,18385,18386} Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, and pro-caspase-6.{6292} Caspase-3 is activated by cleavage events at Asp28/Ser29 (between N-terminal pro-domain) and Asp175/Ser176 (between large and small subunits) to generate a large subunit of 17 kDa and a small subunit of 12 kDa.{18385}
Synonyms: Apopain|CPP32|ICE3|Yama
Immunogen: recombinant full-length human caspase-3
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified IgG in 200 µl PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Isotype: IgG1κ
Applications: IHC (frozen and paraffin-embedded sections) and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Cytosolic & Secreted Proteases