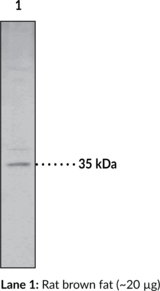
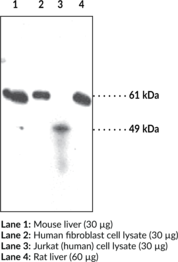
Description
CaMKII is an important member of the calcium/calmodulin-activated protein kinase family, functioning in neural synaptic stimulation and T-cell receptor signaling.{15705,15706} CaMKII is expressed in many different tissues but is specifically found in the neurons of the forebrain and its mRNA is found within the dendrites and the soma of the neuron. The CaMKII that is found in the neurons consists of two subunits of 52 (termed α genes) and 60 kDa (β genes). CaMKII has catalytic and regulatory domains, as well as an ATP-binding domain, and a consensus phosphorylation site.{15707,15708,15709,15710,15711} The binding of Ca2+/calmodulin to its regulatory domain releases its auto inhibitory effect and activates the kinase.{15712} This kinase activation results in autophosphorylation at threonine 286 (Thr286).{15712} The threonine phosphorylation state of CaMKII can be regulated through protein phosphatase 1 (PP1)/protein kinase A (PKA). Whereas PP1 dephosphorylates phospho-CaMKII at Thr286, PKA prevents this dephosphorylation.{15713} Autophosphorylation also enables CaMKII to attain an enhanced affinity for NMDA receptors in postsynaptic densities.{15714,15715,15716}
Synonyms: Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II
Immunogen: synthetic peptide
Formulation: Protein G purified mouse IgG at a concentration of 1 mg/ml in PBS, pH. 7.4, containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA, IF, IP, and WB
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunoprecipitation||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Calcium Mobilization||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|cAMP Signaling||Research Area|Neuroscience