Description
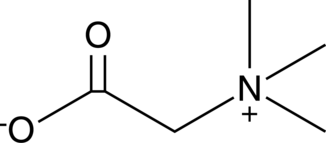
A quaternary ammonium compound with diverse biological activities; has roles in osmoregulation and serves as a methyl donor in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine; reduces serum ALT and AST activity, increases serum HDL levels, decreases serum LDL levels, and reduces hepatic steatosis and inflammation in a mouse model of NAFLD induced by a methionine- and choline-deficient diet at 1.5% w/v in drinking water; reduces plasma levels of tHcy, AdoMet, AdoHcy, and cystathionine and attenuates hypercoagulation in a mouse model of homocystinuria
Formal name: 1-carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-methanaminium, inner salt
Synonyms: Glycine Betaine|N,N,N-Trimethylglycine
Molecular weight: 117.1
CAS: 107-43-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Dyslipidemias||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|NAFLD & NASH