Description
α-methylacyl-Coenzyme A (α-methylacyl-CoA) racemase (AMACR), is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of branched chain fatty acids and 2-arylpropanoic acids (2-APAs), such as ibuprofen (Item No. 70280).{60129} It is expressed in most human tissues and is localized to peroxisomes and mitochondria.{60129,60130} AMACR converts R-2-methyl fatty acids to S-2-methylacyl-CoA esters via an epimerization reaction prior to their degradation by β-oxidation.{60129} AMACR is overexpressed in localized and metastatic prostate cancer, as well as in a variety of other cancers.{60131} AMACR has been found selectively in patient-derived prostate cancer tumor tissue compared to non-cancer prostate tissue, and has been used as a biomarker of the disease.{60132} Mutations in AMACR resulting in reduced enzyme activity lead to the accumulation of R-2-methyl fatty acids and are associated with neurological and peroxisomal disorders.{60133} Cayman’s AMACR (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Synonyms: 2-arylpropionyl-CoA Epimerase|2-R-Ibuprofenyl racemase|P504S|α-methylacyl-CoA
Immunogen: Peptide from the N-terminal region of human p504s
Formulation: 100 µl of protein A-affinity purified antibody
Isotype: IgG
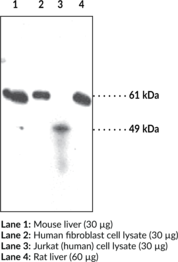
Applications: IHC, WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Inborn Errors of Metabolism||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Fatty Acids|Degradation||Research Area|Neuroscience