Description
A sea sponge metabolite with diverse biological activities; induces cell death in MCF-7 and ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner from 0.25-0.5 μM; blocks EGF-induced endocytosis of EGFR and EGF-dependent cell proliferation in MCF-7 cells; inhibits BAE cell proliferation and cord formation in a Matrigel™ assay; inhibits angiogenesis in a CAM assay from 1.5-3 nmol per egg; has antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria; inhibits HIV-1 replication (IC50 = 14.6 μM) ,
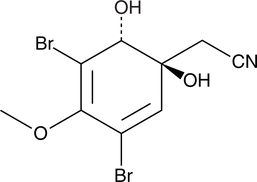
Formal name: (1S,6R)-3,5-dibromo-1,6-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-2,4-cyclohexadiene-1-acetonitrile
Synonyms: NSC 170364
Molecular weight: 339
CAS: 28656-91-9
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antivirals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Angiogenesis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|HIV & AIDS