Description
A 5-HT1A receptor agonist (EC50 = 12 nM in rat hippocampal membranes); enhances the behavioral effects of Δ9-THC in rhesus monkeys in a discriminant stimulus-shock test (0.178 mg/kg, i.v.); reduces baclofen-induced aggression in mice when administered directly to the dorsal raphe nucleus; impairs contextual fear in mice when administered prior to training (0.5 mg/kg, s.c); reduces apnea in a methyl-CpG-binding protein 2-deficient mouse model of Rett syndrome (50 µg/kg i.p.)
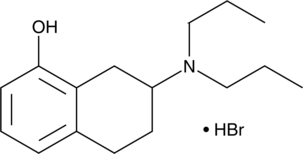
Formal name: 7-(dipropylamino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphthalenol, monohydrobromide
Synonyms: 8-OH-DPAT
Molecular weight: 328.3
CAS: 76135-31-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Cannabinoid Research