Description
A catecholaminergic neurotoxin; has been used to induce dopaminergic lesions and parkinsonian symptoms as a model of Parkinson’s disease in rodents; induces locomotor impairment in mice and loss of tyrosine hydroxylase-reactive neurons in mouse brain when administered into the substantia nigra, MFB, or striatum at doses of 9, 6, and 18 μg, respectively; decreases dopamine and norepinephrine levels in rat brain at 200 μg; induces apoptosis in primary rat cortical cells and PC12 rat adrenal cells at 50 μM; activates caspase-3, -8, and -9 in a time-dependent manner and increases the level of intracellular ROS in PC12 cells at 75 μM; induces apoptosis in rat substantia nigra when stereotaxically injected into the right MFB
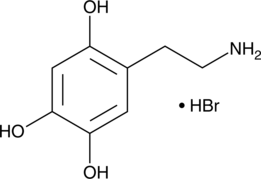
Formal name: 5-(2-aminoethyl)-1,2,4-benzenetriol, monohydrobromide
Synonyms: 2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenethylamine|6-hydroxy Dopamine|Oxidopamine
Molecular weight: 250.1
CAS: 636-00-0
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Toxins||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Cytosolic & Secreted Proteases||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Parkinson’s Disease