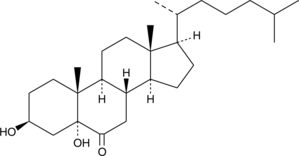
Description
Cholesterol is the most abundant neutral lipid present in the surfactant of the lung epithelial lining fluid. The double bond between carbons 5 and 6 of cholesterol is susceptible to attack by ozone within this surfactant environment. 6-Oxo-3,5,-diol is a major metabolite of cholesterol formed during exposure of lung epithelial cells to ozone, with formation of 5β,6β-epoxycholesterol as a predominant precursor.{13448} Exposure of C57BL/6J mice to 0.5-3 ppm ozone produced a dose-dependent formation of 6-oxo-3,5,-diol which was detectable in the bronchalveolar lavage fluid, lavaged cells, and lung homogenates.{13449} 6-Oxo-3,5-diol is a potent inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis in human bronchial epithelial cells with an IC50 of 350 nM and exhibits significant cytotoxicity in the low µM range.{13448} Therefore, the toxic effects of ozone may be mediated by formation oxysterols of this type.
Formal name: 3β,5α-dihydroxy-cholestan-6-one
Synonyms: 6-Oxo-3,5-diol|Cholestane-6-oxo-3β,5α-diol
Molecular weight: 418.7
CAS: 13027-33-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Sterol Lipids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sterol Biosynthesis||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sterol Lipids||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Lipid Peroxidation