Description
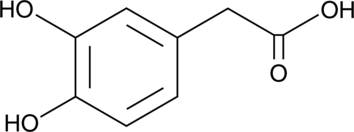
A dopamine metabolite; levels are increased 5- to 6-fold compared to wild-type in the nucleus accumbens, striatum, and prefrontal cortex of COMT knockout mice; oxidized DOPAC binds to monomeric α-synuclein, preventing fibrillation; foot shock stress increases levels relative to control in the prefrontal cortex, olfactory tubercles, and VTA in rats
Formal name: 3,4-dihydroxy-benzeneacetic acid
Synonyms: DOPAC|NSC 73191
Molecular weight: 168.1
CAS: 102-32-9
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Xenobiotic Metabolites||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease