Description
PGE1 is not a major naturally occurring prostaglandin, but it is widely administered clinically for several indications including peripheral occlusive vascular disease, erectile dysfunction, and in neonatal cardiology.{22,3803} The metabolism of PGE1 is normally initiated by oxidation at C-15, resulting in 13,14-dihydro-15-keto PGE1 as the major metabolite. However, inhibition of this pathway or saturation by excess substrate could theoretically lead to enhanced production of 2,3-dinor metabolites, including 2,3-dinor PGE1. The biological activity of 2,3-dinor PGE1 has not been published.
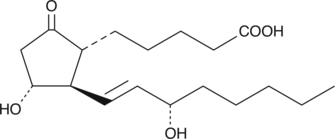
Formal name: 9-oxo-11α,15S-dihydroxy-2,3-dinor-prost-13E-en-1-oic acid
Synonyms: 2,3-dinor PGE1
Molecular weight: 326.4
CAS: 7046-40-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Prostaglandins||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway