Description
A monochlorinated form of palmitic acid; produced in an MPO- and time-dependent manner in neutrophils stimulated by PMA; induces NETosis in human neutrophils, increasing DNA release from neutrophils, colocalization of MPO with ecDNA, and trapping of E. coli at 10 μM; increases COX-2 protein levels in HCAECs at 50 μM; increases production of P-selectin, von Willebrand factor, and angiopoietin-2 in HCAECs, as well as neutrophil and platelet adherence, at 10 μM; induces apoptosis in THP-1 cells and primary human monocytes and increases caspase-3 activity in THP-1 cells at 10-50 μM
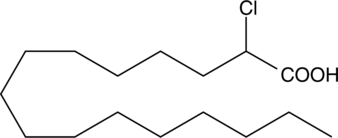
Formal name: 2-chloro-hexadecanoic acid
Synonyms: 2-ClHA|2-CLPA
Molecular weight: 290.9
CAS: 19117-92-1
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Fatty Acids||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Vasculature|Smooth Muscle Cells||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Inflammatory Lipid Mediators|Prostaglandins||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|NETosis||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry